Decentralized apps set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with American high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset. From exploring the innovative technology behind DApps to discussing their impact on various industries, this topic is sure to captivate and inspire curiosity.
As we delve deeper into the world of decentralized apps, a fascinating journey awaits, filled with insights on their development, security measures, and future trends that could shape the digital landscape.
Overview of Decentralized Apps
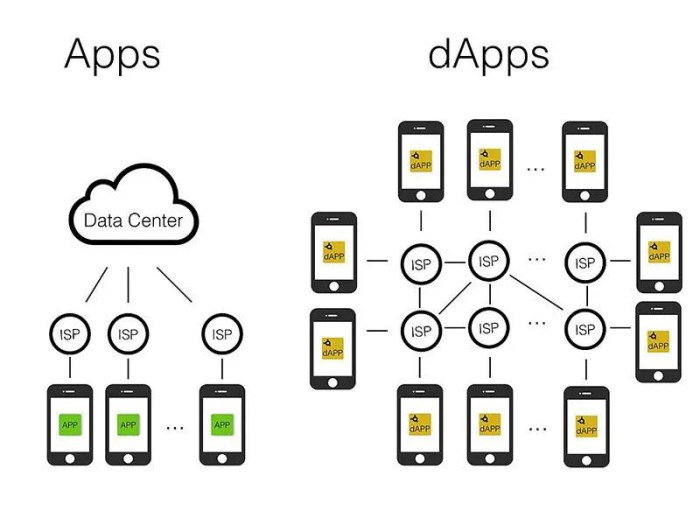
Decentralized apps (DApps) are applications that run on a decentralized network of computers rather than a single central server. This means that DApps are not controlled by any single entity, making them more secure, transparent, and resistant to censorship.
Some popular DApps include:
Examples of Popular DApps and Their Functionalities
- Ethereum – a platform for building smart contracts and decentralized applications.
- Uniswap – a decentralized exchange for trading cryptocurrencies.
- Brave Browser – a privacy-focused web browser that rewards users with cryptocurrency for viewing ads.
The benefits of using DApps compared to centralized applications include:
Benefits of Using DApps
- Enhanced Security: DApps are less vulnerable to hacking attacks due to their decentralized nature.
- Transparency: DApps operate on public blockchains, allowing users to verify transactions and data independently.
- Censorship Resistance: DApps cannot be easily shut down or censored by a single authority.
How Decentralized Apps Work
In the world of Decentralized Apps (DApps), the underlying technology plays a crucial role in their functionality. Let’s dive into how DApps work and the key components that make them operate seamlessly.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology serves as the backbone of DApps, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined rules, automate processes within DApps, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Decentralized Networks
Decentralized networks, such as peer-to-peer networks, support DApps by distributing data and processing power across multiple nodes. This decentralized approach enhances security and resilience, making DApps less vulnerable to single points of failure.
Data Storage and Transactions
Data storage in DApps is decentralized, with information distributed across the network to prevent data loss or manipulation. Transactions in DApps are verified and recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and integrity. Users can interact with DApps securely and directly without relying on centralized entities.
Development of Decentralized Apps
Decentralized applications, or DApps, are built using a variety of programming languages to ensure functionality and efficiency. Commonly used languages in DApp development include:
Programming Languages
- Solidity: A language specifically designed for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum platform.
- JavaScript: Used for developing the front-end of DApps and interacting with smart contracts.
- Python: Known for its versatility, Python can be used for backend development in DApps.
- Rust: Growing in popularity for its speed and security features, Rust is used for blockchain development.
Challenges Faced by Developers
- Security: Ensuring the security of smart contracts and data on the blockchain is a major challenge for DApp developers.
- Scalability: Overcoming scalability issues to handle a large number of users and transactions is crucial for DApp success.
- User Experience: Designing user-friendly interfaces that are intuitive and accessible is essential for mass adoption of decentralized applications.
Best Practices for Designing User-Friendly DApps
- Clear User Interface: Keep the interface simple and intuitive to enhance user experience.
- Transparency: Provide users with clear information about how the DApp works and how their data is being used.
- Responsive Design: Ensure that the DApp is compatible with different devices and screen sizes for a seamless user experience.
- Community Feedback: Gather feedback from users to continuously improve and optimize the DApp for better usability.
Security and Privacy in Decentralized Apps
Decentralized apps (DApps) prioritize security and privacy for users by leveraging blockchain technology. This ensures that user data is protected and transactions are secure.
Ensuring Security and Privacy
- DApps use cryptography to secure data and transactions, making them tamper-proof and resistant to hacks.
- Smart contracts in DApps automatically execute transactions without the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Users have control over their data and can choose what information to share, enhancing privacy.
Vulnerabilities and Developer Responses
- One common vulnerability in DApps is smart contract bugs, which can lead to security breaches. Developers conduct extensive testing and audits to identify and fix these bugs.
- Phishing attacks can also target users of DApps. Developers educate users on best practices to avoid falling victim to such attacks.
- Decentralized storage systems used by DApps may face data breaches. Developers implement encryption and decentralized storage solutions to mitigate this risk.
Comparison with Centralized Applications, Decentralized apps
- Decentralized apps offer greater security as they are not controlled by a single entity, reducing the risk of centralized data breaches.
- Centralized applications rely on centralized servers, making them more vulnerable to cyber attacks and data breaches.
- Decentralized apps prioritize user privacy by giving users control over their data, whereas centralized applications often collect and monetize user data without consent.
Future Trends in Decentralized Apps

In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, decentralized applications (DApps) continue to make waves with their innovative approach to data management and user empowerment. As we look ahead to the future, several trends are expected to shape the development and adoption of DApps in various industries.
Emerging Technologies Impacting DApp Development
- The rise of blockchain interoperability solutions such as Polkadot and Cosmos, enabling DApps to communicate and share data across different blockchain networks seamlessly.
- The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities in DApps to enhance automation, optimize decision-making processes, and personalize user experiences.
- The emergence of decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and governance models, revolutionizing traditional financial services and offering new opportunities for users to engage in decentralized economic activities.
Potential Use Cases for DApps in Various Industries
- In the healthcare sector, DApps could streamline patient data management, ensure data privacy and security, and enable secure sharing of medical records among healthcare providers.
- Within the supply chain industry, DApps could enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency by tracking products from manufacturing to delivery, reducing fraud and improving trust among stakeholders.
- For content creators and artists, DApps could provide a decentralized platform for copyright protection, royalty distribution, and direct engagement with fans, bypassing intermediaries and empowering creators.
Evolution of the Decentralized Applications Landscape
- As DApps continue to gain traction, we can expect a more user-friendly interface and improved scalability to accommodate a larger user base and increase transaction speeds.
- The integration of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) in DApps governance structures, enabling community-driven decision-making processes and enhancing transparency and accountability.
- With the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental consciousness, DApps could incorporate green technologies such as proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint.