Kicking off with decentralized apps, this cutting-edge technology is changing the game in the world of applications. From redefining how data is stored and processed to enhancing security with smart contracts, DApps are leading the way towards a decentralized future.
Exploring the benefits, challenges, and real-world applications of decentralized apps sheds light on the potential they hold for disrupting traditional business models across various industries.
Introduction to Decentralized Apps (DApps)

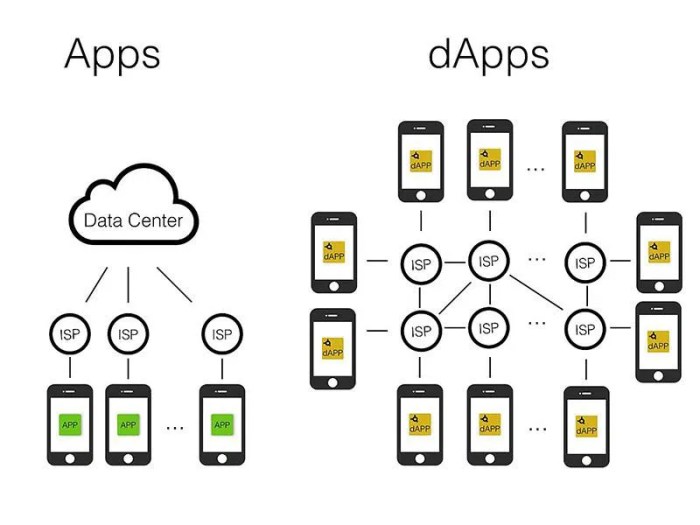
Decentralized Apps, or DApps, are applications that run on a decentralized network of computers rather than a single centralized server. These apps utilize blockchain technology to operate without a central authority, making them secure, transparent, and resistant to censorship.
Key Characteristics of DApps
- Decentralization: DApps operate on a distributed network of nodes, ensuring no single point of failure.
- Open Source: The code of DApps is open for anyone to view and contribute to, promoting transparency and innovation.
- Token Incentives: DApps often use tokens to incentivize users to participate in the network and maintain its integrity.
- Smart Contracts: DApps utilize smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, ensuring trustless interactions.
Benefits of Using DApps
- Enhanced Security: Decentralization reduces the risk of data breaches and hacking attacks.
- Transparency: All transactions on DApps are recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent and immutable record.
- Censorship Resistance: DApps are immune to censorship and government interference, ensuring freedom of expression.
- Lower Costs: By eliminating the need for intermediaries, DApps can reduce transaction fees and operational costs.
Architecture of Decentralized Apps
Decentralized apps, or DApps, have a unique architecture that sets them apart from traditional centralized applications. In a decentralized environment, DApps are not controlled by a single entity or server, but rather run on a distributed network of computers, making them more secure, transparent, and resistant to censorship.
Data storage and processing in decentralized apps are handled through blockchain technology. The blockchain serves as a decentralized ledger that records all transactions and data changes in a secure and transparent manner. Each transaction is verified by network participants, ensuring trust and immutability of the data.
Role of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in supporting DApps by providing a secure and decentralized platform for data storage and processing. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces the risk of data manipulation, and enhances transparency and trust among users. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code, further automate processes and ensure compliance with predefined rules.
Development of Decentralized Apps
Decentralized applications (DApps) are a revolutionary way of building software applications that operate on a decentralized network, rather than a centralized server. This approach offers increased security, transparency, and resilience to censorship. Let’s delve into the development process of DApps.
Common Programming Languages and Frameworks
When it comes to developing DApps, developers often leverage programming languages like Solidity, JavaScript, and Python. Solidity is specifically designed for writing smart contracts on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. Additionally, frameworks such as Truffle and Embark provide tools and libraries to streamline DApp development.
Deploying a Decentralized Application
Deploying a DApp involves uploading the smart contract code to the blockchain network where the application will run. This process typically requires interacting with the blockchain through tools like MetaMask or Remix IDE. Once the code is deployed, users can access the DApp through a compatible web browser with a blockchain wallet extension.
Challenges Faced by Developers
Building DApps comes with its own set of challenges. One major hurdle is ensuring the security of smart contracts, as vulnerabilities can lead to serious financial losses. Scalability is another issue, as blockchain networks can face congestion during times of high activity. Moreover, user adoption and regulatory compliance pose additional challenges for DApp developers.
Use Cases of Decentralized Apps
Decentralized Apps, or DApps, are being utilized across various industries to revolutionize traditional processes and systems. These applications are changing the game in finance, healthcare, supply chain, and more, offering increased security, transparency, and efficiency.
Finance
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a prime example of how DApps are transforming the financial sector. With DApps, individuals can access financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without the need for traditional banks or intermediaries. Smart contracts enable secure transactions and automated processes, providing users with greater control over their assets.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, DApps are streamlining data management and improving patient care. Through blockchain technology, medical records can be securely stored and accessed by authorized individuals, ensuring data privacy and integrity. Additionally, DApps are facilitating telemedicine services and enhancing communication between healthcare providers and patients.
Supply Chain
Supply chain management is another area where DApps are making a significant impact. By utilizing blockchain technology, DApps enable transparent and traceable transactions throughout the supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product to consumers. This increased visibility helps in reducing fraud, improving efficiency, and building trust among stakeholders.
Decentralized App Security
Decentralized applications (DApps) have unique security considerations that differ from traditional centralized apps. Due to their decentralized nature, DApps are more resistant to censorship and single points of failure, but they also come with their own set of vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
Security Considerations for DApps
- Distributed Consensus: DApps rely on distributed consensus mechanisms, such as blockchain, to verify transactions. Ensuring the integrity of this consensus is crucial for the security of the application.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts, which automate processes in DApps, can be vulnerable to bugs and exploits. Proper auditing and testing are essential to mitigate these risks.
- Immutable Data Storage: Once data is stored on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. While this ensures transparency, it also means that any security breaches are permanent.
Role of Smart Contracts in Security
- Code Transparency: Smart contracts are publicly viewable on the blockchain, allowing users to verify the code and ensure that it operates as intended.
- Self-Executing: Smart contracts automatically execute based on predefined conditions, reducing the risk of human error or manipulation.
- Security Audits: Regular security audits of smart contracts can help identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Future Trends in Decentralized Apps
The future of Decentralized Apps (DApps) looks promising as more industries and users are recognizing the benefits of decentralization. Let’s delve into some key trends that could shape the evolution and adoption of DApps in the coming years.
Interoperability Among DApps
Interoperability is expected to be a major trend in the future of DApps. As the number of DApps continues to grow, the ability for different decentralized applications to communicate and interact seamlessly will become crucial. This can lead to a more connected ecosystem where data and assets can flow between different DApps, enhancing the overall user experience.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence, Decentralized apps
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies with DApps is another trend to watch out for. AI can help optimize various processes within decentralized applications, improve decision-making capabilities, and enhance user personalization. This fusion of AI and DApps could lead to more intelligent and efficient decentralized solutions.
Scalability Solutions
Scalability has been a persistent challenge for DApps, especially in terms of transaction speed and throughput. In the future, we can expect to see the emergence of more advanced scalability solutions such as Layer 2 protocols, sharding, and sidechains. These innovations aim to enhance the scalability of DApps, making them more efficient and capable of handling a larger user base.
Enhanced Privacy and Security Features
With growing concerns around data privacy and security, future DApps are likely to focus on implementing enhanced privacy and security features. Technologies like zero-knowledge proofs, homomorphic encryption, and multi-party computation could be integrated into DApps to ensure user data remains secure and confidential. This emphasis on privacy and security will be crucial for gaining user trust and confidence in decentralized applications.
