When it comes to flood insurance policies, understanding the ins and outs is crucial for protecting your property. From coverage details to cost factors, let’s dive into the world of flood insurance policies.
Exploring the different aspects of flood insurance policies can shed light on the importance of this type of coverage and how it differs from homeowners insurance.
Overview of Flood Insurance Policies
Flood insurance policies are specialized insurance plans that provide coverage for property damage caused by flooding. While standard homeowners’ insurance policies typically do not cover flood damage, flood insurance can help protect homeowners, renters, and business owners from the financial burden of repairing or replacing their property after a flood.
Importance of Having Flood Insurance
Having flood insurance is crucial, especially for those living in areas prone to flooding. Without this coverage, individuals may face significant financial losses in the event of a flood. It can help cover the costs of structural repairs, replacing personal belongings, and temporary living expenses.
Types of Properties Covered by Flood Insurance Policies
- Residential Properties: This includes single-family homes, condominiums, and apartments.
- Commercial Properties: Businesses, office buildings, and other commercial structures are also covered.
- Rental Properties: Landlords can also purchase flood insurance to protect their rental properties.
Coverage and Exclusions
When it comes to flood insurance policies, it is important to understand what is typically covered and what exclusions may apply. Let’s dive into the details below.
Coverage Overview
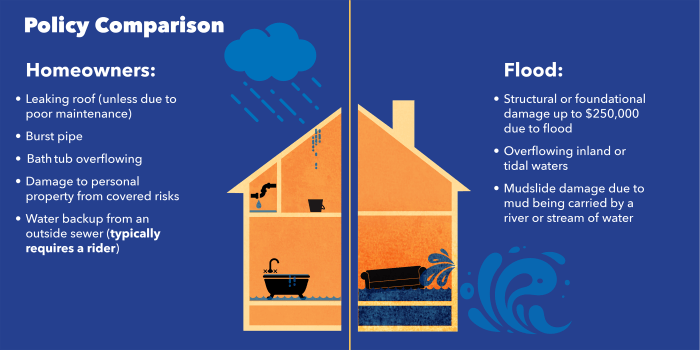
- Flood insurance policies typically cover damage to your home and personal belongings caused by flooding from heavy rain, hurricanes, or other natural disasters.
- Structural damage to your property, including the foundation, walls, and electrical systems, is usually covered.
- Personal belongings such as furniture, appliances, and clothing are also covered under most flood insurance policies.
- Additional living expenses incurred if you need to temporarily relocate due to flood damage may be covered as well.
Common Exclusions
- Damage caused by sewer backups or sump pump failures is typically not covered by standard flood insurance policies.
- Landscaping, decks, patios, and other external structures may not be covered under a flood insurance policy.
- Business interruption losses and financial investments are usually excluded from coverage.
- Damage caused by gradual seepage of water or water leaks from plumbing may be excluded from coverage.
Private vs. Government-Backed Policies
- Private flood insurance policies are offered by private insurance companies and may provide more flexibility in coverage options and limits.
- Government-backed flood insurance policies, such as those offered through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), have standardized coverage limits and premiums.
- Private policies may offer higher coverage limits for both building and contents compared to government-backed policies.
- Government-backed policies are often more affordable for properties located in high-risk flood zones, as they are subsidized by the federal government.
Cost and Premiums
Flood insurance premiums can vary based on several factors that determine the cost of coverage. Understanding how these premiums are determined and what can affect them is crucial for homeowners looking to protect their property from flood damage.
Factors Determining Flood Insurance Premiums
- Location: Properties located in high-risk flood zones will typically have higher premiums compared to those in lower-risk areas.
- Property Value: The value of your home and belongings will also impact the cost of your flood insurance policy.
- Coverage Amount: The level of coverage you choose will influence the premium you pay.
- Building Structure: The type of building and its construction materials can affect premiums.
Tips to Lower Flood Insurance Premiums
- Invest in Flood Mitigation Measures: Installing flood barriers, elevating utilities, and other preventive measures can help lower premiums.
- Apply for FEMA Grants: The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) offers grants for flood mitigation efforts that can reduce insurance costs.
- Choose a Higher Deductible: Opting for a higher deductible can lower your premium, but make sure you can afford the out-of-pocket expense in case of a claim.
- Check for Discounts: Some insurance companies offer discounts for certain mitigation efforts or if your property is located in a lower-risk area.
Making a Claim
After experiencing flood damage, policyholders need to take immediate action to file a flood insurance claim. This process can be overwhelming, but it is crucial to follow the necessary steps to ensure a smooth and successful claim.
Filing a Flood Insurance Claim, Flood insurance policies
- Notify your insurance company as soon as possible after the flood occurs. Provide them with all the necessary details about the damage.
- Document the damage by taking photos or videos of the affected areas. This will help support your claim and provide evidence of the extent of the damage.
- Make a list of all damaged items and include their value. Keep all receipts and records of the items affected by the flood.
- Cooperate with the insurance adjuster assigned to your claim. They will assess the damage and determine the coverage amount based on your policy.
- Review your flood insurance policy to understand the coverage limits, exclusions, and deductibles. This will help you manage your expectations during the claims process.
Common Challenges in Making Flood Insurance Claims
- Delays in processing claims due to a high volume of claims after a widespread flood event.
- Disputes over the extent of damage and the coverage provided by the policy.
- Incomplete documentation or lack of evidence to support the claim, leading to claim denial or reduced payouts.
- Misunderstanding of policy terms and exclusions, resulting in unexpected claim outcomes.
- Difficulty in proving the cause of the damage was indeed a result of a flood, especially in cases of mixed water sources or gradual water damage.
Comparison with Homeowners Insurance
When it comes to protecting your home from unexpected disasters, it’s important to understand the differences between flood insurance and homeowners insurance.
Flood insurance is a separate policy specifically designed to cover damage caused by flooding, such as heavy rains, storm surges, or overflowing rivers. It is not typically included in standard homeowners insurance policies.
On the other hand, homeowners insurance typically covers damage from perils like fire, theft, and windstorms. However, it usually does not cover flood damage, which is why it’s important to have a separate flood insurance policy if you live in a flood-prone area.
When Both Types of Insurance May Be Necessary
In scenarios where both types of insurance may be necessary, consider the following examples:
- If your home is located in a high-risk flood zone, you will likely need a flood insurance policy to protect your property from flood damage.
- Even if you don’t live in a flood-prone area, a sudden and unexpected heavy rainstorm can still cause flooding, making flood insurance a valuable addition to your homeowners coverage.
- In some cases, mortgage lenders may require you to have flood insurance if your home is located in a designated flood hazard area.



